Overview
Every developer understands that in order to optimize something, you must first measure it. The same principle applies to you cloud costs - measuring them is crucial for optimization.
Now you can easily monitor you cloud costs with Coroot.
Don't underestimate the power of simple optimizations - they can be highly effective. When it comes to cloud costs, removing unused resources is often more effective than optimizing your code.
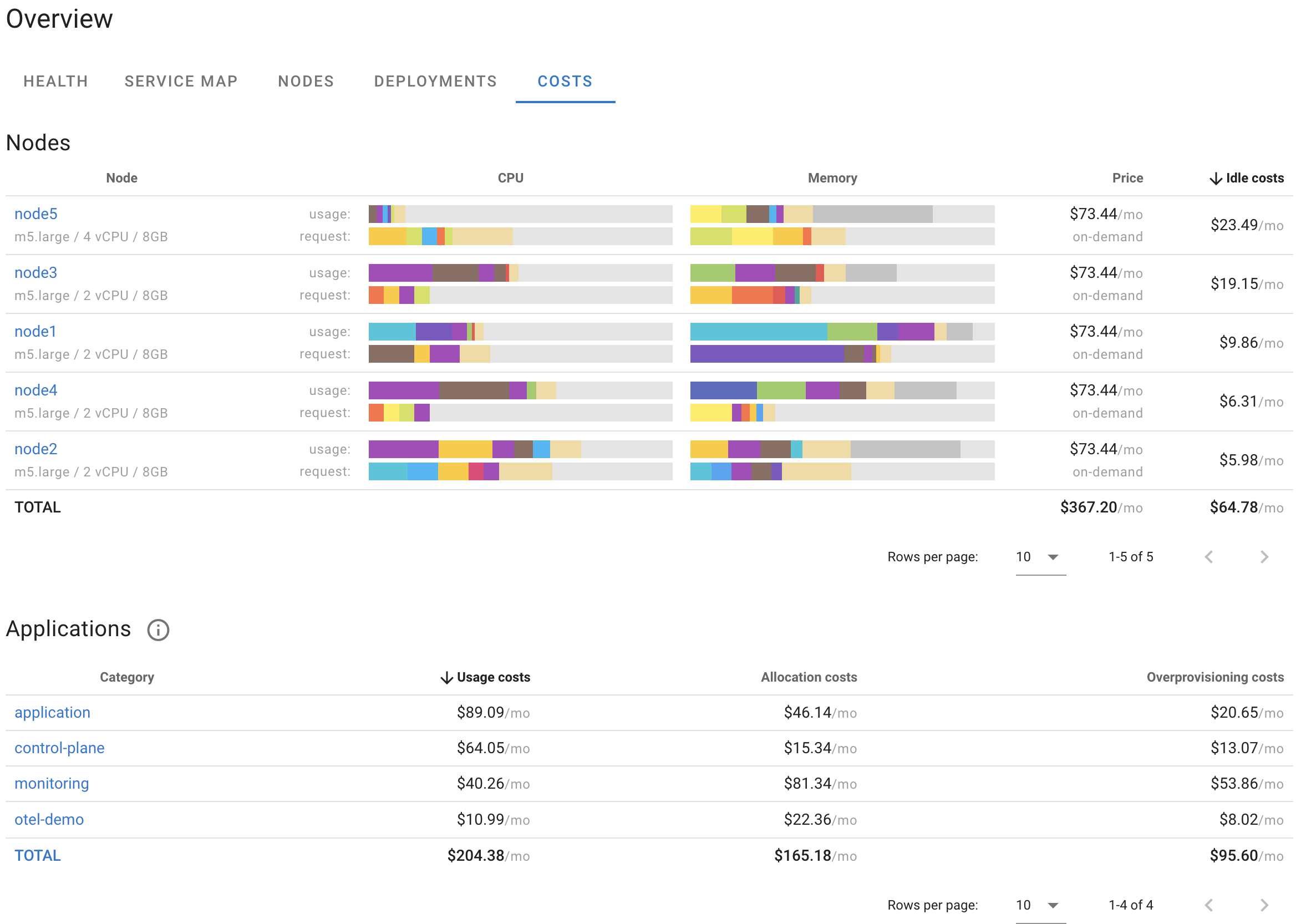
Nodes
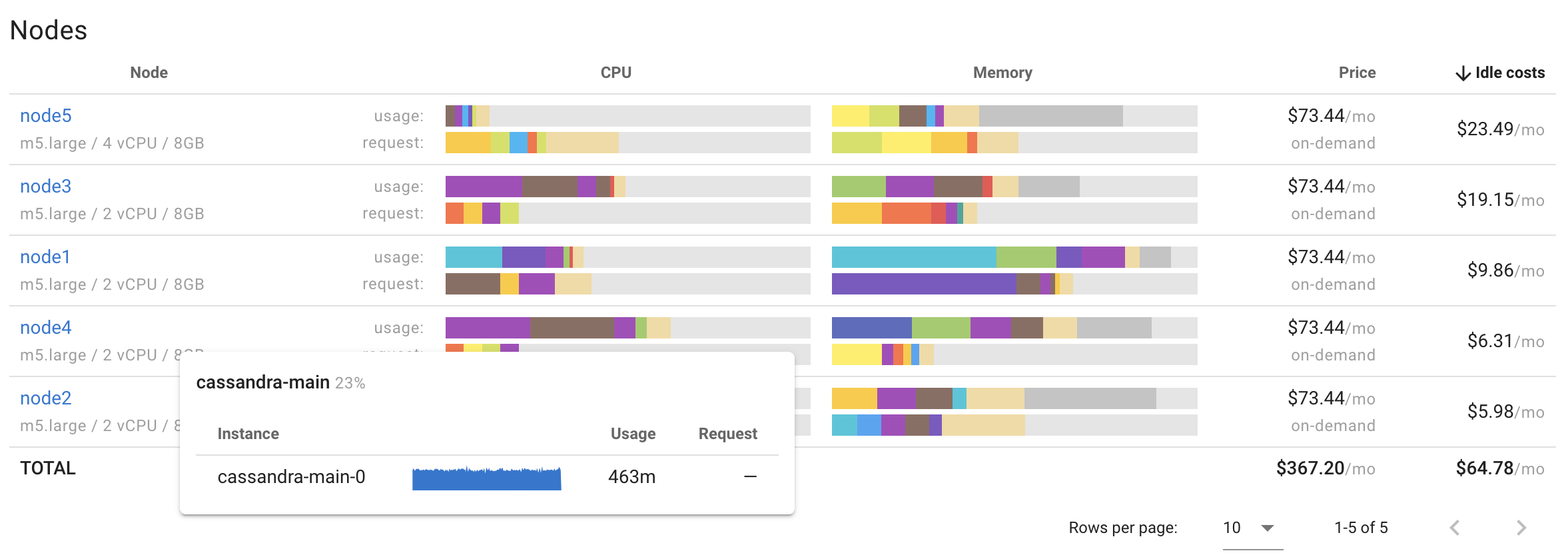
By breaking down costs by nodes, you can easily identify the least utilized nodes (by sorting the table according to Idle costs), understand the usage of each node based on actual CPU/memory usage and requests, and determine which resources are overprovisioned (requested but not used).
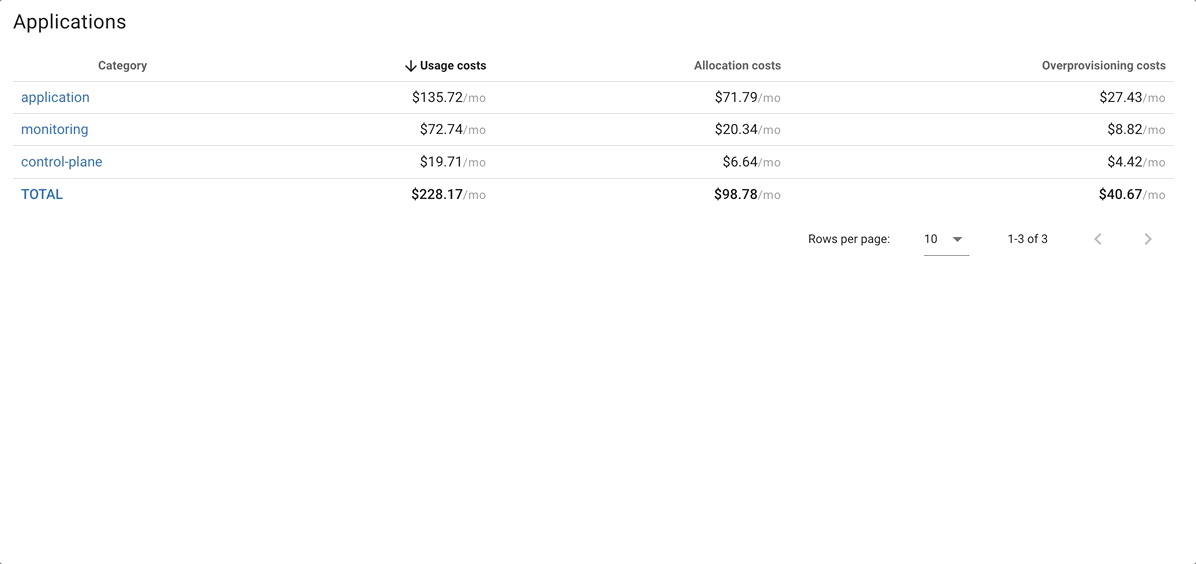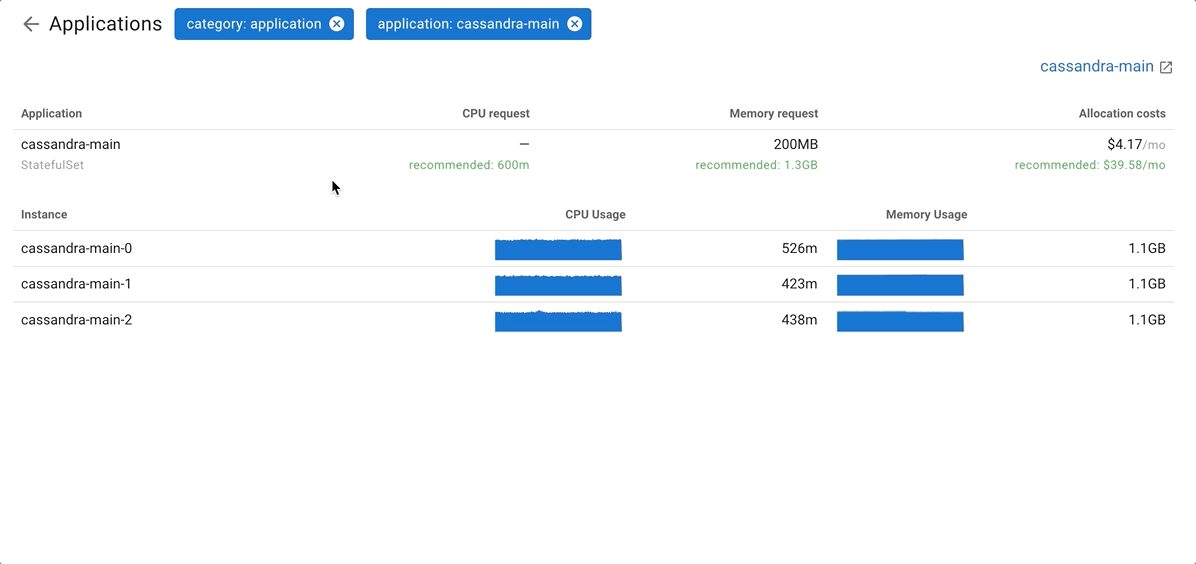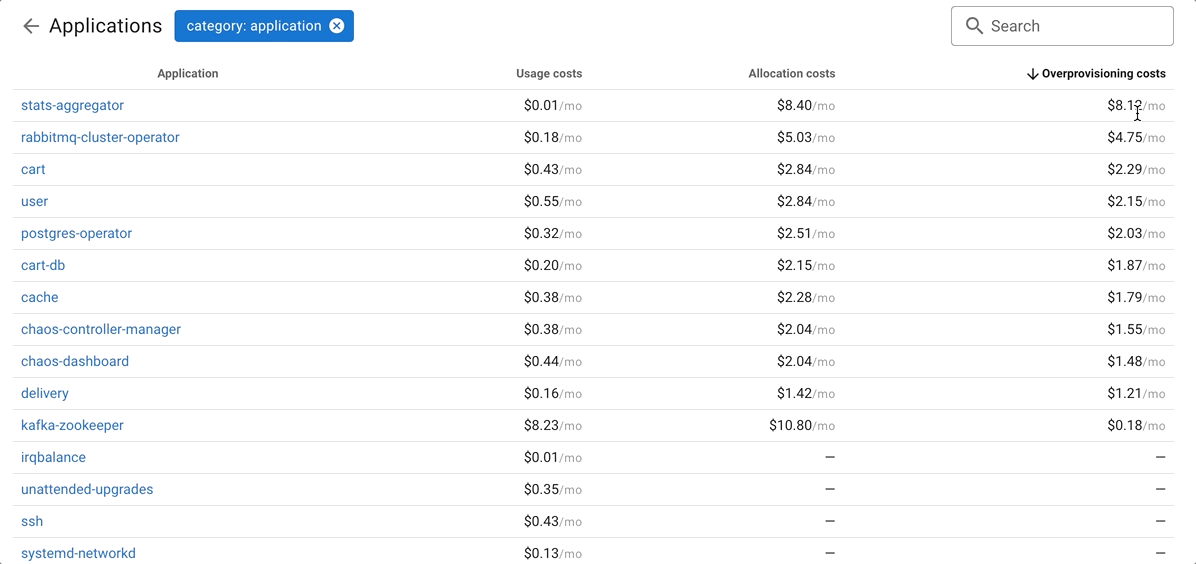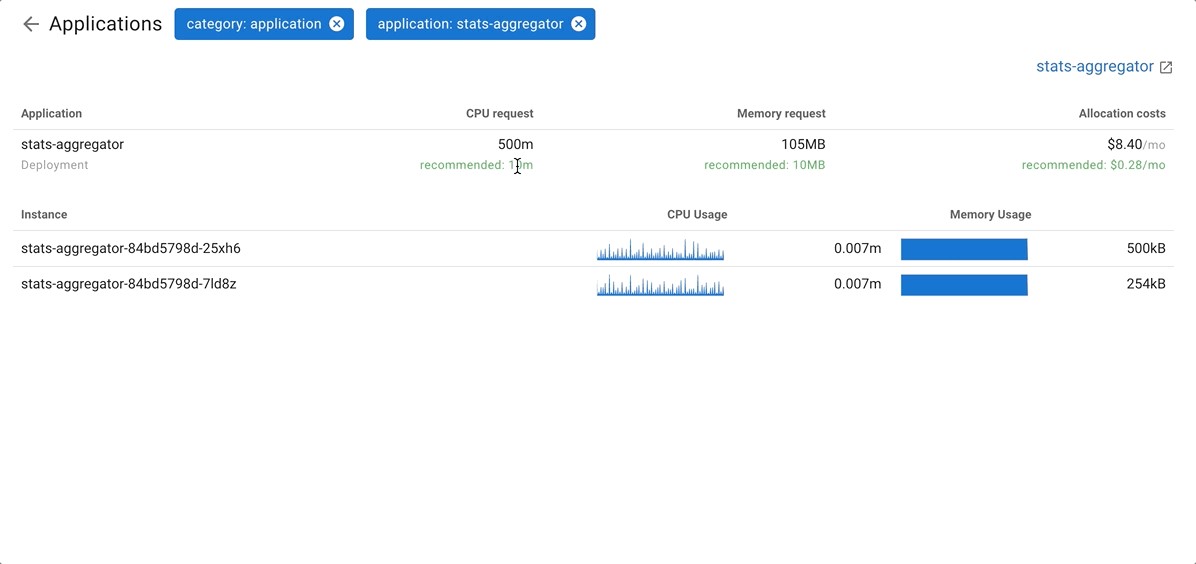
Applications
Coroot simplifies the monitoring of large infrastructures by introducing the concept of application categories.
By default, Coroot automatically categorizes apps related to control-plane and monitoring,
but you can customize your categories easily by defining masks for application names and namespaces.
Coroot breaks down costs by categories, but you can easily drill down to any category and view cost allocations by application.
- Usage Costs: actual CPU/Memory usage of the application multiplied by the resource cost on a specific node.
- Allocation Costs: requested resources (CPU/Memory request in Kubernetes) by the application multiplied by the resource cost on a specific node.
- Overprovisioning Costs: difference between Allocation Costs and Usage Costs for the application. This indicates that the app requested more resources than its actual usage.
Deployment tracking
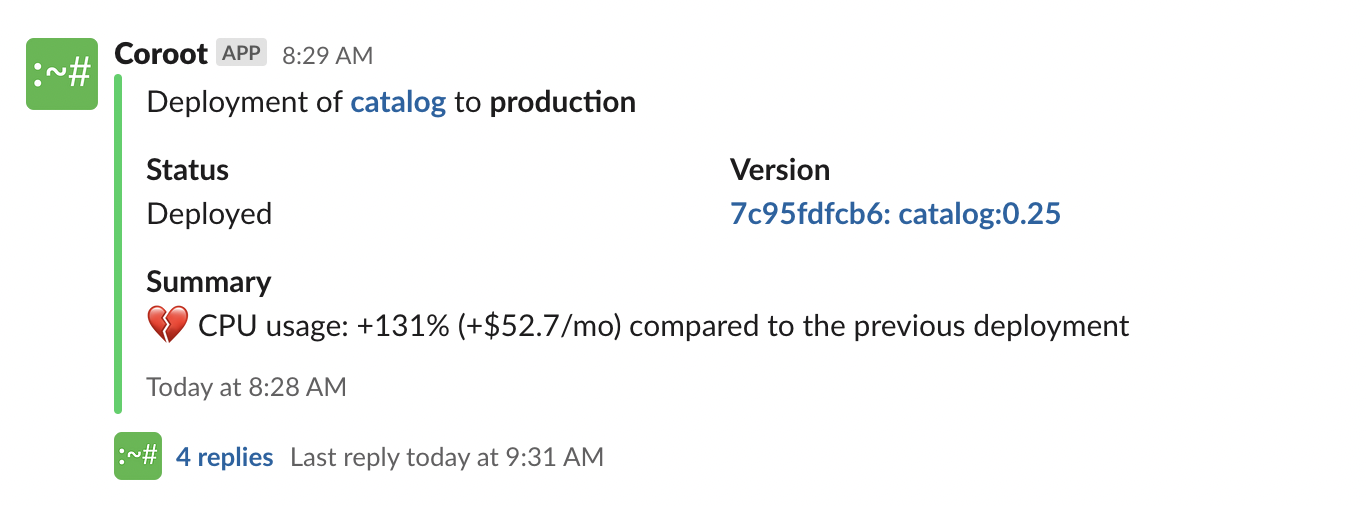
Cost monitoring is also integrated with Deployment Tracking. If a service starts consuming significantly more CPU time than the previous version, you will immediately see an estimated change in costs.
How it works
Coroot's node-agent gathers cloud instance metadata of every node and exports it as the node_cloud_info metric.
With this metric, Coroot can determine the cloud provider, region, type, and purchase options (on-demand/spot/reserved) for each instance.
By leveraging this information, it can quickly determine the price of each node.
To calculate the cost of each resource separately, Coroot assumes that 1 CPU core costs the same as 1GB of memory. By doing so, the CPU and memory usage of every application can be easily translated into $$$.
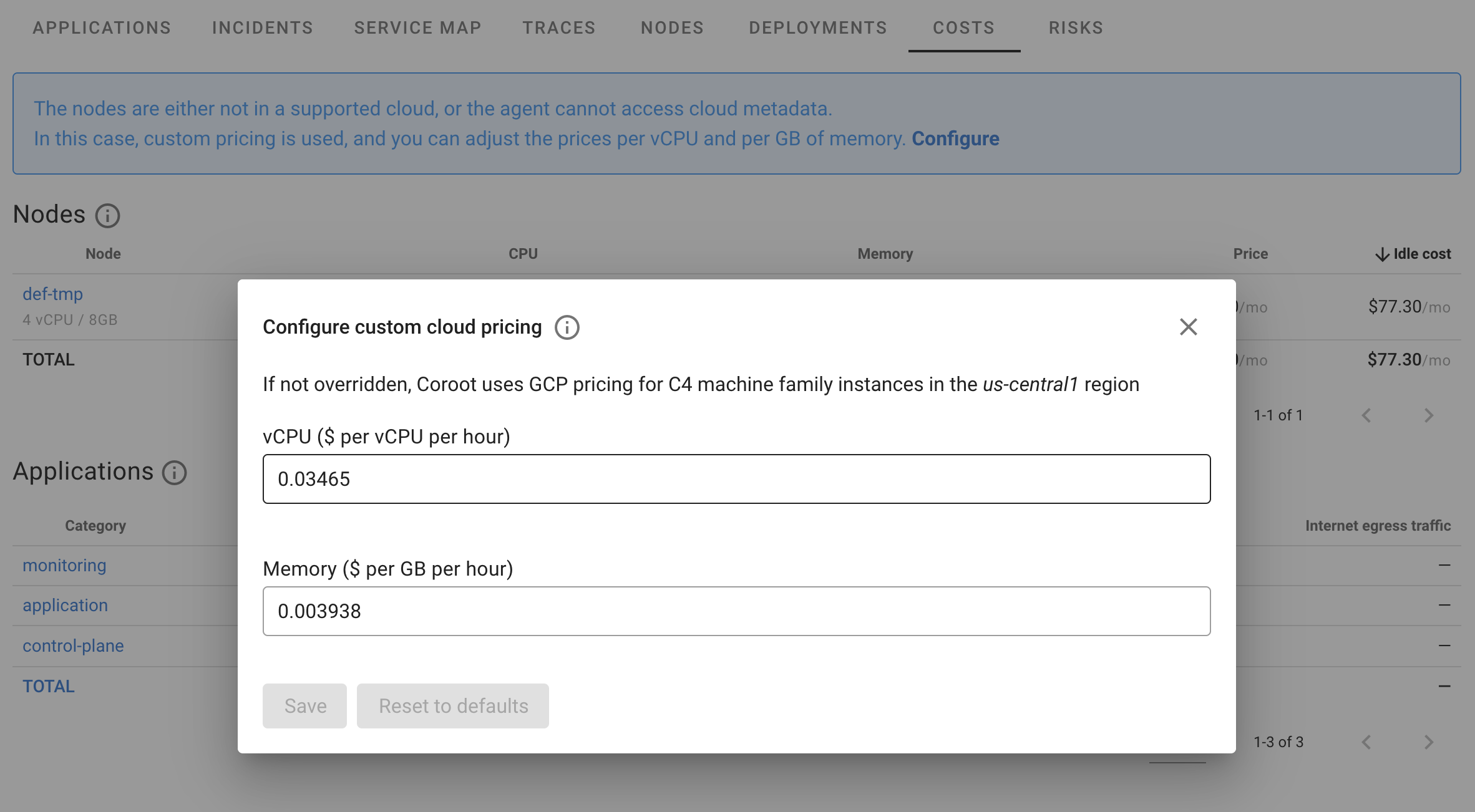
Custom cloud pricing
Out of the box, Coroot supports pricing models for AWS, GCP, and Azure. For nodes not running in these clouds, Coroot uses predefined prices based on GCP’s C4 machine family in the us-central1 region. These prices can be adjusted in the UI.
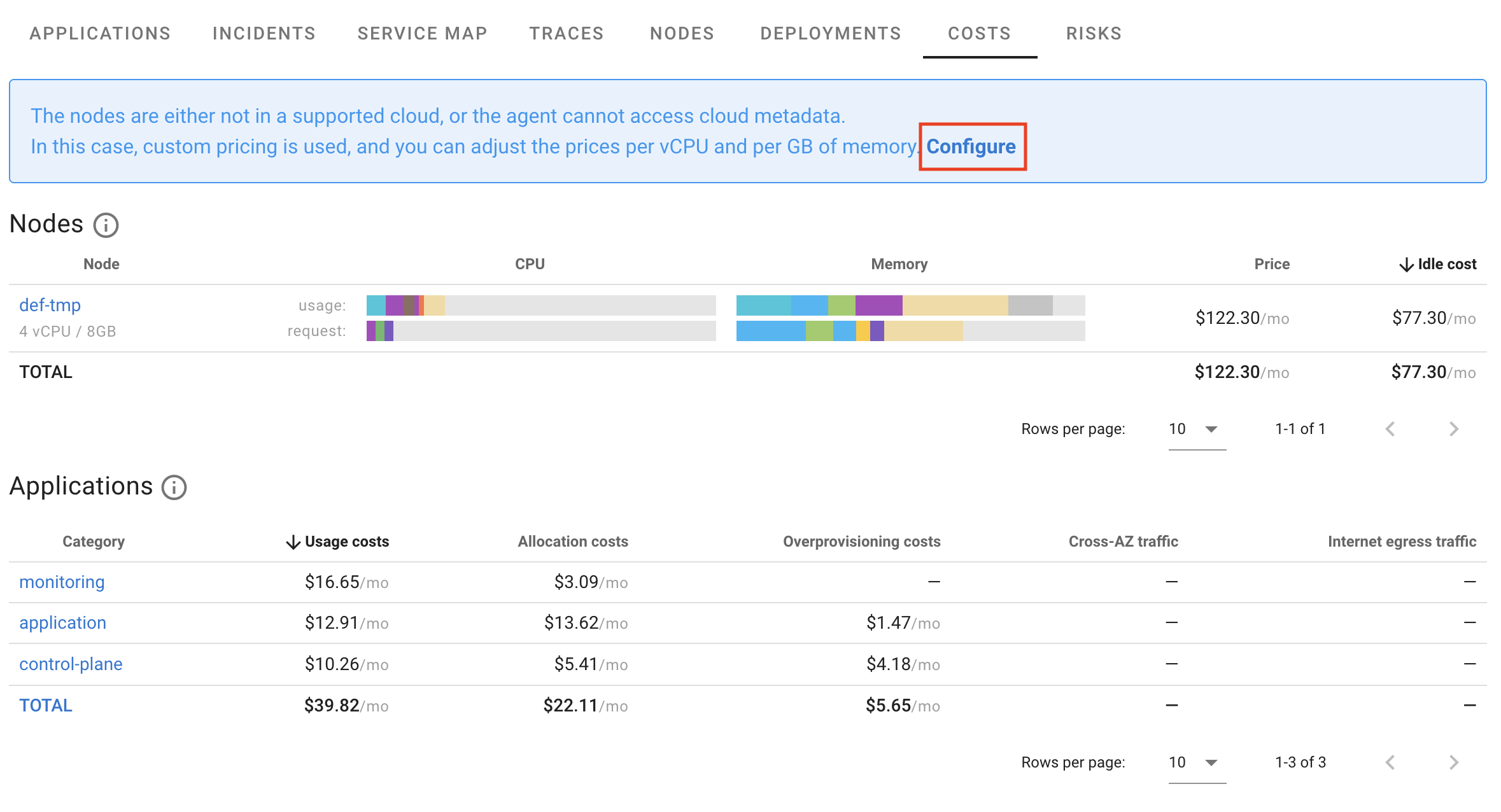
The prices are defined per hour, based on a single vCPU and 1 GB of memory.
Limitations
Coroot has some limitations that are important to note.
- Standard pricing (without discounts)
- The cost calculation considers only CPU, Memory usage and Traffic (egress, cross-AZ) (support for GPUs and volumes will be added later)
- Currently, the cost calculation considers only compute, AWS RDS, and AWS ElastiCache instances (support for EKS/AKS/GKE will be added later)
- Reserved instances are not supported yet